Dnsmasq is a widely used open-source Domain Name System (DNS) forwarding application commonly installed on routers, operating systems, access points, and other networking equipment. Multiple organizations, operating systems and products were affected by the DNSpooq vulnerability. Attackers can use to launch DNS Cache Poisoning, denial of service, and possibly remote code execution attacks on affected devices.
According to advisory, two issues were listed:
- CVE-2020-25684, CVE-2020-25685 and CVE-2020-25686 address the issue of subtle errors in dnsmasq’s protections against the chronic weakness of the DNS protocol to cache-poisoning attacks, the Birthday attack, Kaminsky, etc.
- CVE-2020-25681, CVE-2020-25682, CVE-2020-25683 and CVE-2020-25687 address a set of errors leading to old fashioned buffer overflow in dnsmasq’s DNSSEC code. If DNSSEC validation is enabled, an installation is at risk.
Based on CVSS score from 8.1 to 4, following are the list of CVEs that are collectively called as DNSpooq.
| Sr. No. | CVE | Description |
| 1 | CVE-2020-25681 | Dnsmasq versions before 2.83 are susceptible to a heap-based buffer overflow in sort_rrset() when DNSSEC is used allowing a remote attacker to write arbitrary data into target device’s memory. Thiscan lead to memory corruption and other unexpected behaviors on the target device. |
| 2 | CVE-2020-25682 | Dnsmasq versions before 2.83 are susceptible to buffer overflow in the extract_name() function due to missing length check, when DNSSEC is enabled allowing a remote attacker to cause memory corruption on the target host. |
| 3 | CVE-2020-25683 | Dnsmasq versions before 2.83 are susceptible to a heap-based buffer overflow when DNSSEC is enabled. A remote attacker, who can create valid DNS replies, could use this flaw to cause an overflow in a heap-allocated memory. This flaw is caused by the lack of length checks in rfc1035.c:extract_name(), which could be abused to make the code execute memcpy() with a negative size in get_rdata() and cause a crash in dnsmasq, resulting in a Denial of Service (DoS). |
| 4 | CVE-2020-25687 | Dnsmasq versions before 2.83 are vulnerable to a heap-based buffer overflow with large memcpy in sort_rrset() when DNSSEC is enabled. A remote attacker, who can create valid DNS replies, could use this flaw to cause an overflow in a heap-allocated memory. This flaw is caused by the lack of length checks in rfc1035.c:extract_name(), which could be abused to make the code execute memcpy() with a negative size in sort_rrset() and cause a crash in dnsmasq, resulting in a DoS. |
| 5 | CVE-2020-25684 | A lack of proper address/port check implemented in dnsmasq versions |
| 6 | CVE-2020-25685 | A lack of query resource name (RRNAME) checks implemented in dnsmasq’s versions before 2. |
| 7 | CVE-2020-25686 | Multiple DNS query requests for the same resource name (RRNAME) by dnsmasq versions before 2.83 allows for remote attackers to spoof DNS traffic, using a birthday attack (RFC 5452), that can lead to DNS cache poisoning. |
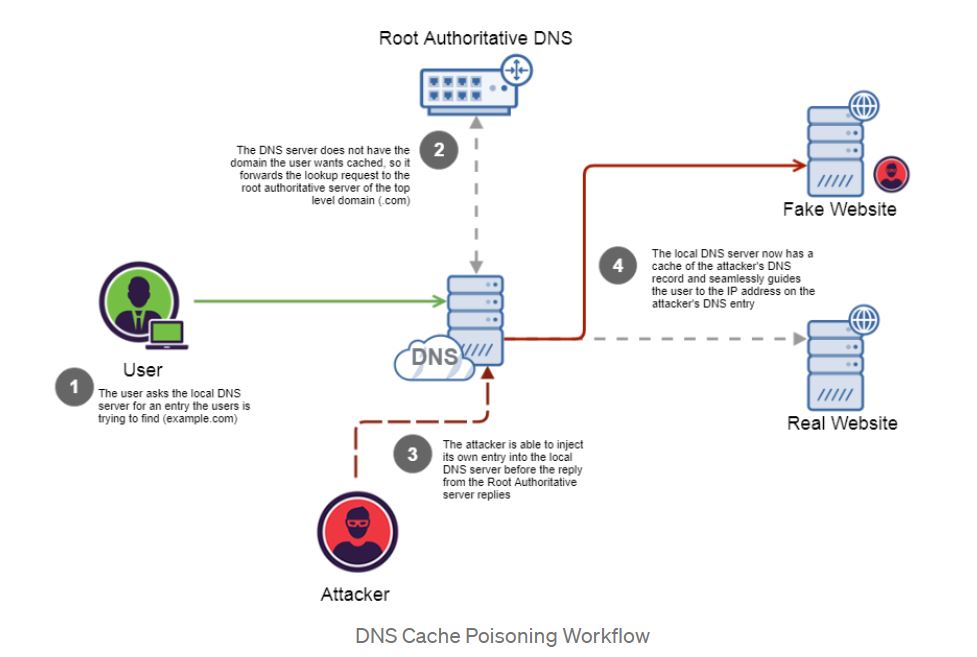
Image Source: Medium
Affected Products:
Arista
This vulnerability affects all EOS products including the 7xxx and 7xx Series switches and routers, and all CloudEOS packaging options.
Cisco
Around 55 Cisco products and services are affected by the dnsmasq vulnerabilities.
OpenWrt
OpenWrt version 19.07.0 to 19.07.5 are affected
NetGear
RAX40 running firmware versions prior to v1.0.3.88
RAX35 running firmware versions prior to v1.0.3.88
Red Hat
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6
Siemens
RUGGEDCOM RM1224
SCALANCE M-800
SCALANCE S615
SCALANCE SC-600
SCALANCE W1750D
Sophos RED
Synology
DSM 6.2
SRM 1.2
Ubuntu
Multiple versions
Solution
Multiple products were affected and list of advisories for each of them were published to resolve the vulnerabilities. Arista, Cisco, Dnsmasq, OpenWRT, NetGear, Red Hat, Siemens, Sophos, Synology, and Ubuntu are some organizations that have released patches to address DNSpooq vulnerability.
Detection
Qualys customers can scan their network with QID(s) 38825, 280834, 158991, 158982, 174554, 174553, 174552, 239019, 239018, 239015, 239014, 239013 and 239012 to detect vulnerable assets.
Please continue to follow Qualys Threat Protection for more coverage on latest vulnerabilities.
References and Sources
https://www.jsof-tech.com/disclosures/dnspooq/
https://medium.com/iocscan/dns-cache-poisoning-bea939b5afaf
https://www.jsof-tech.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/DNSpooq_Technical-Whitepaper.pdf
https://www.kb.cert.org/vuls/id/434904
https://www.arista.com/en/support/advisories-notices/security-advisories/12135-security-advisory-61
http://lists.thekelleys.org.uk/pipermail/dnsmasq-discuss/2021q1/014599.html
https://openwrt.org/advisory/2021-01-19-1
https://www.netgear.com/support/
https://access.redhat.com/security/vulnerabilities/RHSB-2021-001
https://cert-portal.siemens.com/productcert/pdf/ssa-646763.pdf