Fortinet released a security advisory to address a zero-day vulnerability tracked as CVE-2024-55591. The vulnerability has a critical severity rating with a CVSS score of 9.6. Successful exploitation of the vulnerability may allow a remote attacker to gain super-admin privileges via crafted requests to the Node.js websocket module.
Fortinet mentioned in the advisory that the authentication bypass zero-day vulnerability is exploited in the wild. Attackers are exploiting the vulnerability to hijack Fortinet firewalls and breach enterprise networks.
CISA added the CVE-2024-55591 to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog, acknowledging its active exploitation. CISA urged users to patch the vulnerability before January 21, 2025.
As per Fortinet, attackers are exploiting the vulnerability to create randomly generated admin or local users on compromised devices. Further, they add these accounts to the existing SSL VPN user groups or new ones.
Attackers can also add or modify firewall policies and other settings. Attackers can also log in to SSLVPN using previously created rogue accounts.
The brain of Fortinet Security Fabric is its network operating system, FortiOS. The Security Fabric’s operating system, or software, connects all its parts and ensures tight integration throughout the deployment of the Security Fabric across an enterprise.
FortiProxy is a secure web proxy that protects employees against internet-borne attacks using several detection methods like web filtering, DNS filtering, data loss prevention, antivirus, intrusion prevention, and sophisticated threat protection.
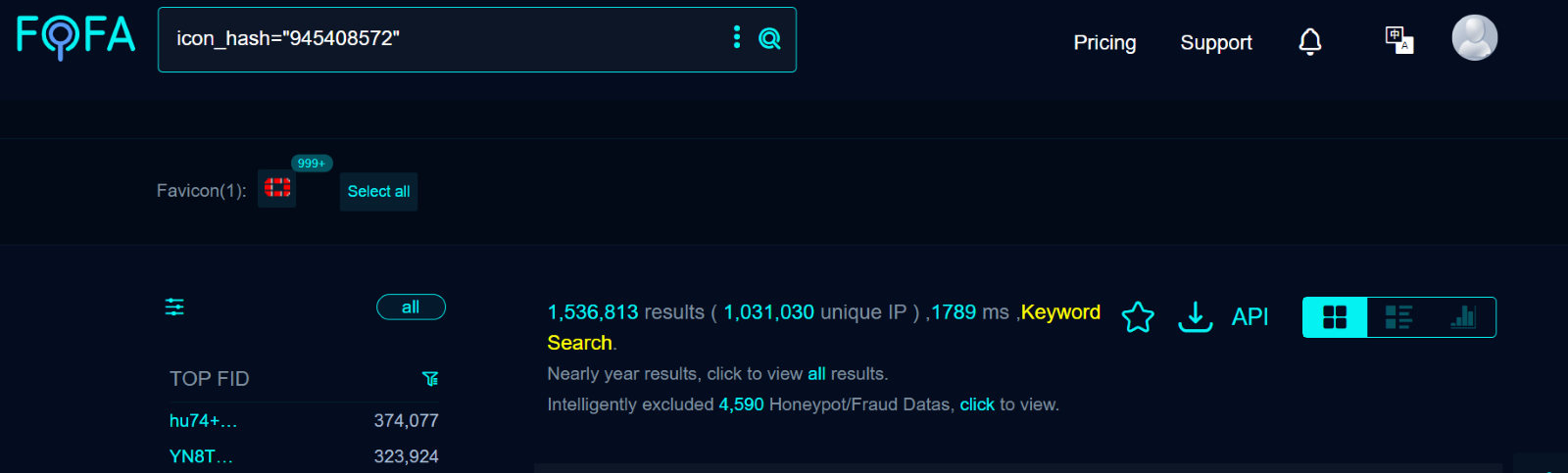
A quick search revealed more than 1,500,000 targets on Fofa at the time of writing.
Affected Versions
- FortiOS 7.0.0 through 7.0.16
- FortiProxy 7.2.0 through 7.2.12
- FortiProxy 7.0.0 through 7.0.19
Mitigation
Customers should upgrade to the following versions to patch the vulnerability:
- FortiOS 7.0.17 or later
- FortiProxy 7.2.13 or later
- FortiProxy 7.0.20 or later
Please refer to the Fortinet PSIRT Advisory (FG-IR-24-535) for more information.
Workaround
Fortinet suggests the following workarounds to address the vulnerability:
Disable HTTP/HTTPS administrative interface
OR
Limit IP addresses that can reach the administrative interface via local-in policies:
config firewall address edit "my_allowed_addresses" set subnet end
Then, create an Address Group:
config firewall addrgrp edit "MGMT_IPs" set member "my_allowed_addresses" end
Create the Local in Policy to restrict access only to the predefined group on the management interface (here: port1):
config firewall local-in-policy edit 1 set intf port1 set srcaddr "MGMT_IPs" set dstaddr "all" set action accept set service HTTPS HTTP set schedule "always" set status enable next
edit 2 set intf "all" set srcaddr "all" set dstaddr "all" set action deny set service HTTPS HTTP set schedule "always" set status enable end
If using non-default ports, create an appropriate service object for GUI administrative access:
config firewall service custom edit GUI_HTTPS set tcp-portrange 443 next
edit GUI_HTTP set tcp-portrange 80 end
Qualys Detection
Qualys customers can scan their devices with QIDs 44501 and 152625 to detect vulnerable assets.
Please continue to follow Qualys Threat Protection for more coverage of the latest vulnerabilities.