As the second Patch Tuesday of 2025 arrives, Microsoft has released crucial updates to strengthen cybersecurity defenses. Let’s explore the highlights and what they mean for users.
Microsoft Patch’s Tuesday, February 2025 edition addressed 67 vulnerabilities, including three critical and 53 important severity vulnerabilities. In this month’s updates, Microsoft has addressed four zero-day vulnerabilities, two of which have been actively exploited in attacks and two publicly disclosed.
Microsoft has addressed 10 vulnerabilities in Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) in this month’s updates.
Microsoft Patch Tuesday, February edition includes updates for vulnerabilities in Microsoft Streaming Service, Windows LDAP – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, Windows NTLM, Windows DHCP Server, Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based), Microsoft PC Manager, and more.
Microsoft has fixed several flaws in multiple software, including Spoofing, Denial of Service (DoS), Elevation of Privilege (EoP), Information Disclosure, and Remote Code Execution (RCE).
The February 2025 Microsoft vulnerabilities are classified as follows:
| Vulnerability Category | Quantity | Severities |
| Spoofing Vulnerability | 3 | Important: 3 |
| Denial of Service Vulnerability | 9 | Important: 9 |
| Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 19 | Important: 19 |
| Information Disclosure Vulnerability | 1 | Important: 1 |
| Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 22 | Critical: 3 Important: 19 |
| Security Feature Bypass | 2 | Important: 2 |
Zero-day Vulnerabilities Patched in February Patch Tuesday Edition
CVE-2025-21391: Windows Storage Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
Windows Storage is a feature of Windows operating systems that manages how data is stored on a computer. It includes Storage Spaces, which combine physical and virtual disks to improve performance and protect data.
The vulnerability does not allow an attacker to disclose any confidential information. The vulnerability may allow an attacker to delete data, which could lead to the service’s unavailability.
CISA added the CVE-2025-21391 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog and requested users to patch it before March 4, 2025.
CVE-2025-21418: Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
The ‘Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock is a core Windows system driver. This is a crucial component in the network communication process. The driver provides a low-level functionality to the WinSock API, allowing applications to interact with network sockets.
Successful exploitation of the vulnerability may allow an attacker to gain SYSTEM privileges.
CISA added the CVE-2025-21418 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog and requested users to patch it before March 4, 2025.
CVE-2025-21377: NTLM Hash Disclosure Spoofing Vulnerability
An NTLM hash is a cryptographic representation of a user’s password stored on Windows systems. It is a vital part of the process used to authenticate a user on Windows systems.
An attacker may exploit the vulnerability to disclose a user’s NTLMv2 hash. Upon successful exploitation, an attacker may authenticate as the user.
CVE-2025-21194: Microsoft Surface Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
Microsoft Surface is a family of touchscreen-based personal computers, tablets, and interactive whiteboard hardware products. Most of them run the Windows operating system and use Intel processors.
Successful exploitation of the vulnerability requires an attacker to gain access to the restricted network before running an attack.
Critical Severity Vulnerabilities Patched in February Patch Tuesday Edition
CVE-2025-21379: DHCP Client Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
A DHCP Client Service refers to the software component on a computer that allows it to automatically acquire network configuration details like an IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway from a DHCP server on the network.
The vulnerability can be exploited by a machine-in-the-middle (MITM) attack. The vulnerability is only limited to systems connected to the same network segment as the attacker. The vulnerability cannot be exploited across multiple networks (for example, a WAN) and would be limited to systems on the same network switch or virtual network.
CVE-2025-21376: Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a standard network protocol that allows users to access and manage information within a directory service. The protocol provides a way to centrally store and manage user information across a network, often used for authentication and single sign-on (SSO) purposes within a company.
An attacker must win a race condition to exploit the vulnerability successfully. An unauthenticated attacker could exploit the vulnerability by sending a specially crafted request to a vulnerable LDAP server. Successful exploitation may lead to a buffer overflow, which could be leveraged to execute remote code.
CVE-2025-21381: Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet program that allows users to create, edit, analyze, and present data. It’s part of the Microsoft Office and Microsoft 365 suites.
Successful exploitation of the vulnerability may allow an attacker to achieve remote code execution.
Other Microsoft Vulnerability Highlights
- CVE-2025-21358 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Windows Core Messaging. Upon successful exploitation, an attacker may gain SYSTEM privileges.
- CVE-2025-21184 & CVE-2025-21414 are elevation of privilege vulnerability in Windows Core Messaging. An attacker must gather information specific to the environment and take additional actions before exploitation to prepare the target environment for successful exploitation. Upon successful exploitation, an attacker may gain SYSTEM privileges.
- CVE-2025-21420 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in the Windows Disk Cleanup Tool. Successful exploitation of the vulnerability may allow an attacker to gain SYSTEM privileges.
- CVE-2025-21400 is a remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint Server. In a network-based attack, an authenticated attacker, with Site Owner permission, could write arbitrary code to inject and execute code on the SharePoint Server.
- CVE-2025-21419 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Windows Setup Files Cleanup. An attacker who exploits the vulnerability may delete targeted files on a system.
- CVE-2025-21367 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in the Windows Win32 Kernel Subsystem. Upon successful exploitation, an attacker may gain SYSTEM privileges.
Microsoft Release Summary
This month’s release notes cover multiple Microsoft product families and products/versions affected, including, but not limited to, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Sales, Windows DHCP Client, Windows Message Queuing, Windows Resilient File System (ReFS) Deduplication Service, Windows Core Messaging, Azure Network Watcher, Windows Telephony Service, Microsoft Surface, Microsoft High Performance Compute Pack (HPC) Linux Node Agent, Windows Telephony Server, Visual Studio, Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS), Windows Internet Connection Sharing (ICS), Microsoft Windows, Windows Update Stack, Windows Remote Desktop Services, Windows Kerberos, Active Directory Domain Services, Windows Kernel, Windows Win32 Kernel Subsystem, Microsoft Digest Authentication, Windows Installer, Microsoft Office Excel, Windows Storage, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Office SharePoint, Windows DWM Core Library, Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock, Windows Setup Files Cleanup, Windows Disk Cleanup Tool, Microsoft AutoUpdate (MAU), Visual Studio Code.
Discover and Prioritize Vulnerabilities in Vulnerability Management, Detection & Response (VMDR)
Qualys VMDR automatically detects new Patch Tuesday vulnerabilities using continuous updates to its Knowledgebase (KB).
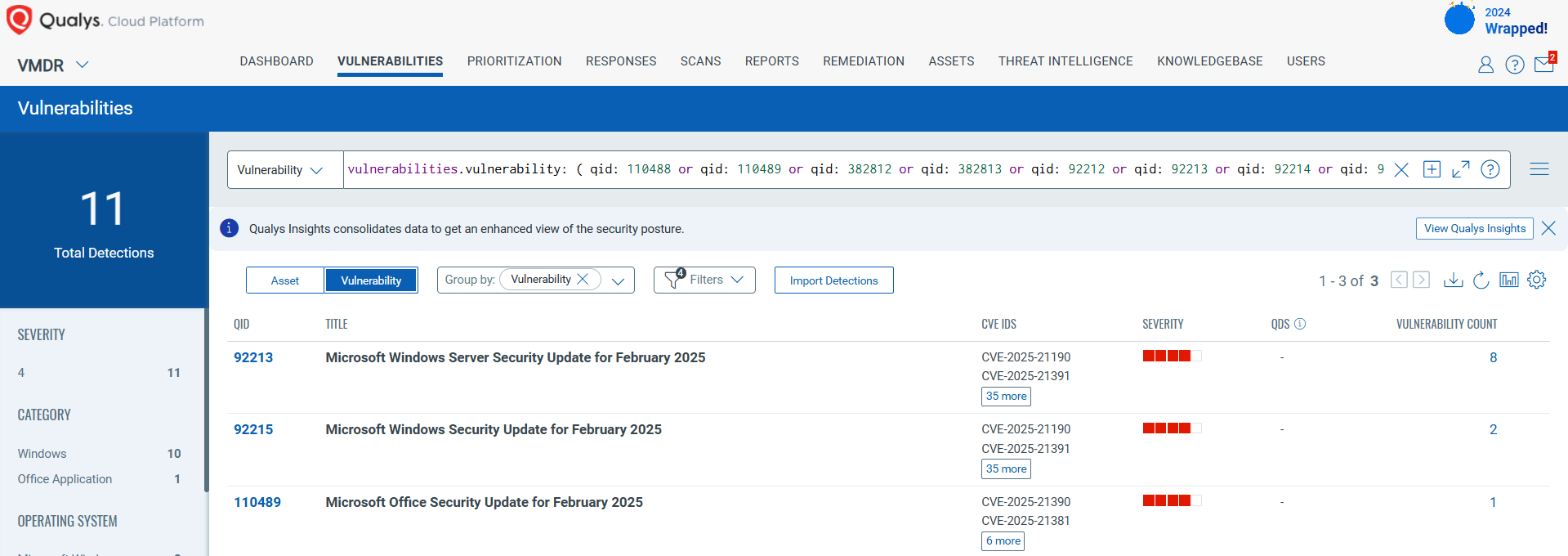
You can see all your impacted hosts by these vulnerabilities using the following QQL query:
vulnerabilities.vulnerability: ( qid: 110488 or qid: 110489 or qid: 382812 or qid: 382813 or qid: 92212 or qid: 92213 or qid: 92214 or qid: 92215 )
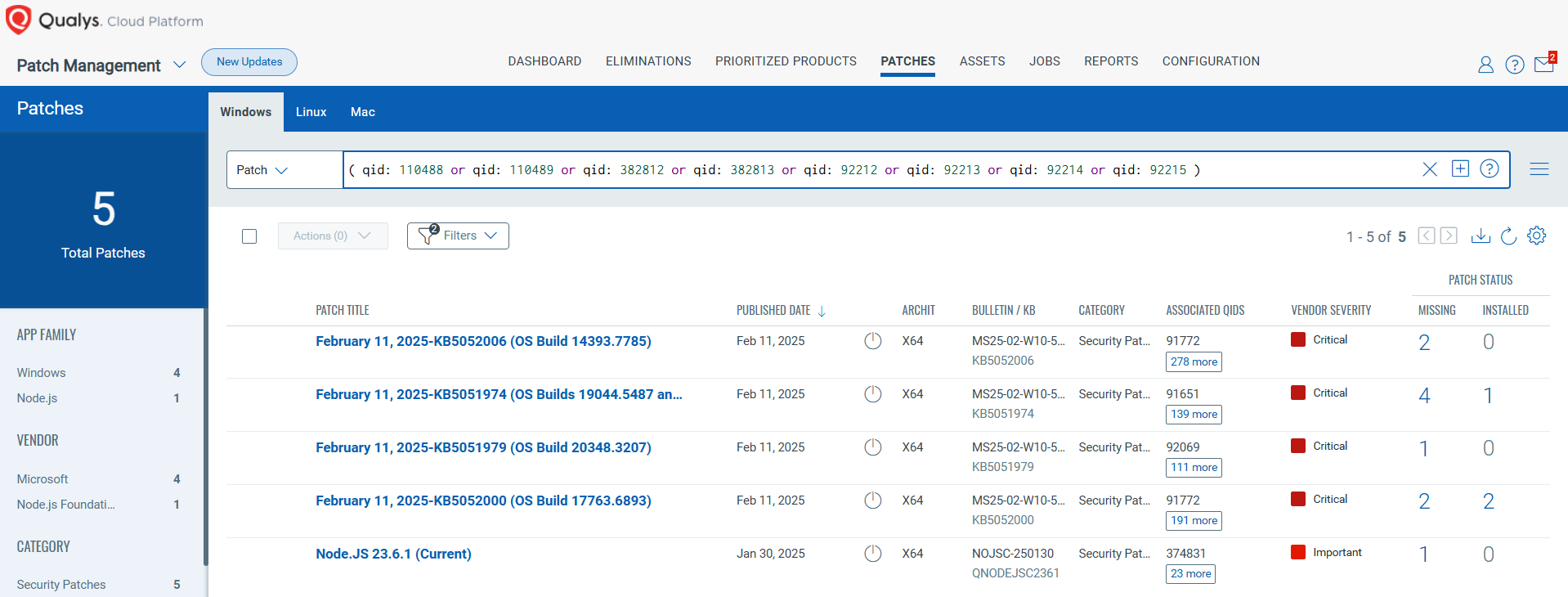
Rapid Response with Patch Management (PM)
VMDR rapidly remediates Windows hosts by deploying the most relevant and applicable per-technology version patches. You can simply select respective QIDs in the Patch Catalog and filter on the “Missing” patches to identify and deploy the applicable, available patches with one click.
The following QQL will return the missing patches for this Patch Tuesday:
( qid: 110488 or qid: 110489 or qid: 382812 or qid: 382813 or qid: 92212 or qid: 92213 or qid: 92214 or qid: 92215 )
Visit the February 2025 Security Updates page to access the full description of each vulnerability and the systems it affects.
Qualys customers can scan their network with QIDs 110488, 110489, 382812, 382813, 92212, 92213, 92214, and 92215 to detect vulnerable assets.
Please continue to follow Qualys Threat Protection for more coverage of the latest vulnerabilities.
References:
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/releaseNote/2025-Feb
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2025-21379
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2025-21376
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2025-21381
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-21391
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-21418
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-21377
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-21194