Microsoft’s April 2025 Patch Tuesday has arrived, delivering critical security updates and fixes across the various products, features, and roles. Here’s a quick breakdown of what you need to know.
In this month’s Patch Tuesday, April 2025 edition, Microsoft addressed 134 vulnerabilities, including 11 critical and 110 important severity vulnerabilities. In this month’s updates, Microsoft has addressed one zero-day vulnerability being exploited in the wild.
Microsoft has addressed 12 vulnerabilities in Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) in this month’s updates.
Microsoft Patch Tuesday, April edition includes updates for vulnerabilities in Windows Hyper-V, Remote Desktop Gateway Service, Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS), Windows Common Log File System Driver, Windows TCP/IP, Visual Studio, Windows Active Directory Certificate Services, Windows Kerberos, Windows Kernel, and more.
Microsoft has fixed several flaws in multiple software, including Spoofing, Denial of Service (DoS), Elevation of Privilege (EoP), Information Disclosure, and Remote Code Execution (RCE).
The April 2025 Microsoft vulnerabilities are classified as follows:
| Vulnerability Category | Quantity | Severities |
| Spoofing Vulnerability | 1 | Important: 1 |
| Denial of Service Vulnerability | 14 | Important: 14 |
| Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 49 | Important: 49 |
| Information Disclosure Vulnerability | 17 | Important: 17 |
| Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 31 | Critical: 20 Important: 11 |
| Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | 9 | Important: 9 |
Zero-day Vulnerabilities Patched in April Patch Tuesday Edition
CVE-2025-29824: Windows Common Log File System Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
The Common Log File System (CLFS) is a general-purpose logging service used by software clients running in user or kernel mode. CLFS can be used for data management, database systems, messaging, Online Transactional Processing (OLTP), and other transactional systems.
The use after free flaw in the Windows Common Log File System Driver could allow an authenticated attacker to elevate privileges locally. Upon successful exploitation, an attacker may gain SYSTEM privileges.
CISA added the CVE-2025-29824 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog, acknowledging its active exploitation. CISA urges users to patch the vulnerability before April 29, 2025.
Critical Severity Vulnerabilities Patched in April Patch Tuesday Edition
CVE-2025-26686: Windows TCP/IP Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol and is a suite of communication protocols used to interconnect network devices on the Internet. TCP/IP is also used as a communications protocol in a private computer network — an intranet or extranet.
An attacker must win a race condition to exploit the vulnerability. Sensitive data storage in improperly locked memory in Windows TCP/IP allows an unauthorized attacker to execute code over a network.
CVE-2025-27752: Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
The heap-based buffer overflow flaw in Microsoft Office Excel could allow an unauthenticated attacker to achieve remote code execution.
CVE-2025-29791: Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
The type confusion in Microsoft Office Excel could allow an unauthenticated attacker to achieve remote code execution.
CVE-2025-27491: Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Hyper-V is Microsoft’s hardware virtualization product that allows users to create and run virtual machines (VMs) on Windows Server and Windows 10/11. The product enables better hardware utilization and resource management.
An attacker must win a race condition to exploit the vulnerability. The use after free flaw in Windows Hyper-V could allow an authenticated attacker to achieve remote code execution.
CVE-2025-27745, CVE-2025-27748, and CVE-2025-27749: Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
The use after free flaw in Microsoft Office could allow an unauthenticated attacker to achieve remote code execution.
CVE-2025-27480: Windows Remote Desktop Services Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
The use after free flaw in Remote Desktop Gateway Service could allow an unauthenticated attacker to execute code remotely. An attacker could successfully exploit this vulnerability by connecting to a system with the Remote Desktop Gateway role, triggering the race condition to create a use-after-free scenario, and then execute arbitrary code.
CVE-2025-27482: Windows Remote Desktop Services Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
In Remote Desktop Gateway Service, sensitive data storage in improperly locked memory can allow an unauthenticated attacker to execute remote code.
CVE-2025-26663 and CVE-2025-26670: Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Client Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
An LDAP client is a software application or tool that uses the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) to interact with a directory service, enabling tasks like searching, retrieving, and managing information stored in a hierarchical structure.
The use after free flaw in Lightweight Directory Access Protocol could allow an unauthenticated attacker to achieve remote code execution. An unauthenticated attacker may exploit the vulnerabilities by sending specially crafted requests to a vulnerable LDAP server.
Other Microsoft Vulnerability Highlights
- CVE-2025-27727 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Windows Installer. An attacker may exploit the vulnerability to gain SYSTEM privileges.
- CVE-2025-29792 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Microsoft Office. Upon successful exploitation, an attacker could gain SYSTEM privileges.
- CVE-2025-29793 is a remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint. An authenticated attacker with Site Owner permissions may exploit the vulnerability to execute code remotely in the context of SharePoint Server.
- CVE-2025-29794 is a remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint. An authenticated attacker with Site Owner permissions may exploit the vulnerability to execute code remotely in the context of SharePoint Server.
- CVE-2025-29809 is a security feature bypass vulnerability in Windows Kerberos. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could bypass the Windows Defender Credential Guard feature to leak Kerberos’s credentials.
- CVE-2025-27472 is a security feature bypass vulnerability in Windows Mark of the Web. Protection mechanism failure in Windows Mark of the Web (MOTW) could allow an unauthenticated attacker to bypass a security feature over a network.
- CVE-2025-29812 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in the DirectX Graphics Kernel. An attacker may exploit the vulnerability to gain SYSTEM privileges.
Microsoft Release Summary
This month’s release notes cover multiple Microsoft product families and products/versions affected, including, but not limited to, Visual Studio Code, Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service, Windows Local Security Authority (LSA), Windows NTFS, Windows Update Stack, Windows Telephony Service, Windows DWM Core Library, Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based), Azure Local Cluster, Windows Hello, Windows BitLocker, Windows USB Print Driver, Windows Digital Media, Windows Cryptographic Services, Microsoft Office, Windows Secure Channel, Windows Local Session Manager (LSM), Windows LDAP – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, Windows upnphost.dll, Windows Media, Windows Remote Desktop Services, Windows Subsystem for Linux, Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC), RPC Endpoint Mapper Service, Windows Win32K – GRFX, ASP.NET Core, Microsoft Virtual Hard Drive, Microsoft Streaming Service, Windows Mark of the Web (MOTW), Windows HTTP.sys, Windows Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) Device Host, Remote Desktop Client, Azure Local, Windows Bluetooth Service, Windows Installer, Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers, Windows Shell, OpenSSH for Windows, Windows Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) Enclave, Windows Power Dependency Coordinator, Windows Security Zone Mapping, Windows Resilient File System (ReFS), System Center, Microsoft Office Word, Microsoft Office Excel, Microsoft Office SharePoint, Microsoft Edge for iOS, Microsoft AutoUpdate (MAU), Visual Studio Tools for Applications and SQL Server Management Studio, Outlook for Android, Active Directory Domain Services, Windows Mobile Broadband, Windows Kernel Memory, Power Automate, Azure Portal Windows Admin Center, Dynamics Business Central, and Microsoft Office OneNote.
Discover and Prioritize Vulnerabilities in Vulnerability Management, Detection & Response (VMDR)
Qualys VMDR automatically detects new Patch Tuesday vulnerabilities using continuous updates to its Knowledgebase (KB).
You can see all your impacted hosts by these vulnerabilities using the following QQL query:
vulnerabilities.vulnerability: ( qid: 100423 or qid: 110491 or qid: 110492 or qid: 383057 or qid: 383058 or qid: 92234 or qid: 92235 or qid: 92236 or qid: 92237 or qid: 92239 or qid: 92241 or qid: 92242 )

Rapid Response with Patch Management (PM)
VMDR rapidly remediates Windows hosts by deploying the most relevant and applicable per-technology version patches. You can simply select respective QIDs in the Patch Catalog and filter on the “Missing” patches to identify and deploy the applicable, available patches with one click.
The following QQL will return the missing patches for this Patch Tuesday:
( qid: 100423 or qid: 110491 or qid: 110492 or qid: 383057 or qid: 383058 or qid: 92234 or qid: 92235 or qid: 92236 or qid: 92237 or qid: 92239 or qid: 92241 or qid: 92242 )

EVALUATE Vendor-Suggested Mitigation with Policy Compliance (PC)
With Qualys Policy Compliance’s Out-of-the-Box Mitigation or Compensatory Controls reduce the risk of a vulnerability being exploited because the remediation (fix/patch) cannot be done now, these security controls are not recommended by any industry standards such as CIS, DISA-STIG.
Qualys Policy Compliance team releases these exclusive controls based on Vendor-suggested Mitigation/Workaround.
Mitigation refers to a setting, common configuration, or general best practice, existing in a default state, that could reduce the severity of exploitation of a vulnerability.
A workaround is a method, sometimes used temporarily, for achieving a task or goal when the usual or planned method isn’t working. Information technology often uses a workaround to overcome hardware, programming, or communication problems. Once a problem is fixed, a workaround is usually abandoned.
The following Qualys Policy Compliance Control IDs (CIDs), and System Defined Controls (SDC) have been updated to support Microsoft recommended mitigation(s) for this Patch Tuesday.
CVE-2025-21197: Windows NTFS Information Disclosure Vulnerability
This vulnerability has a CVSS: 3.1 6.5 / 5.7
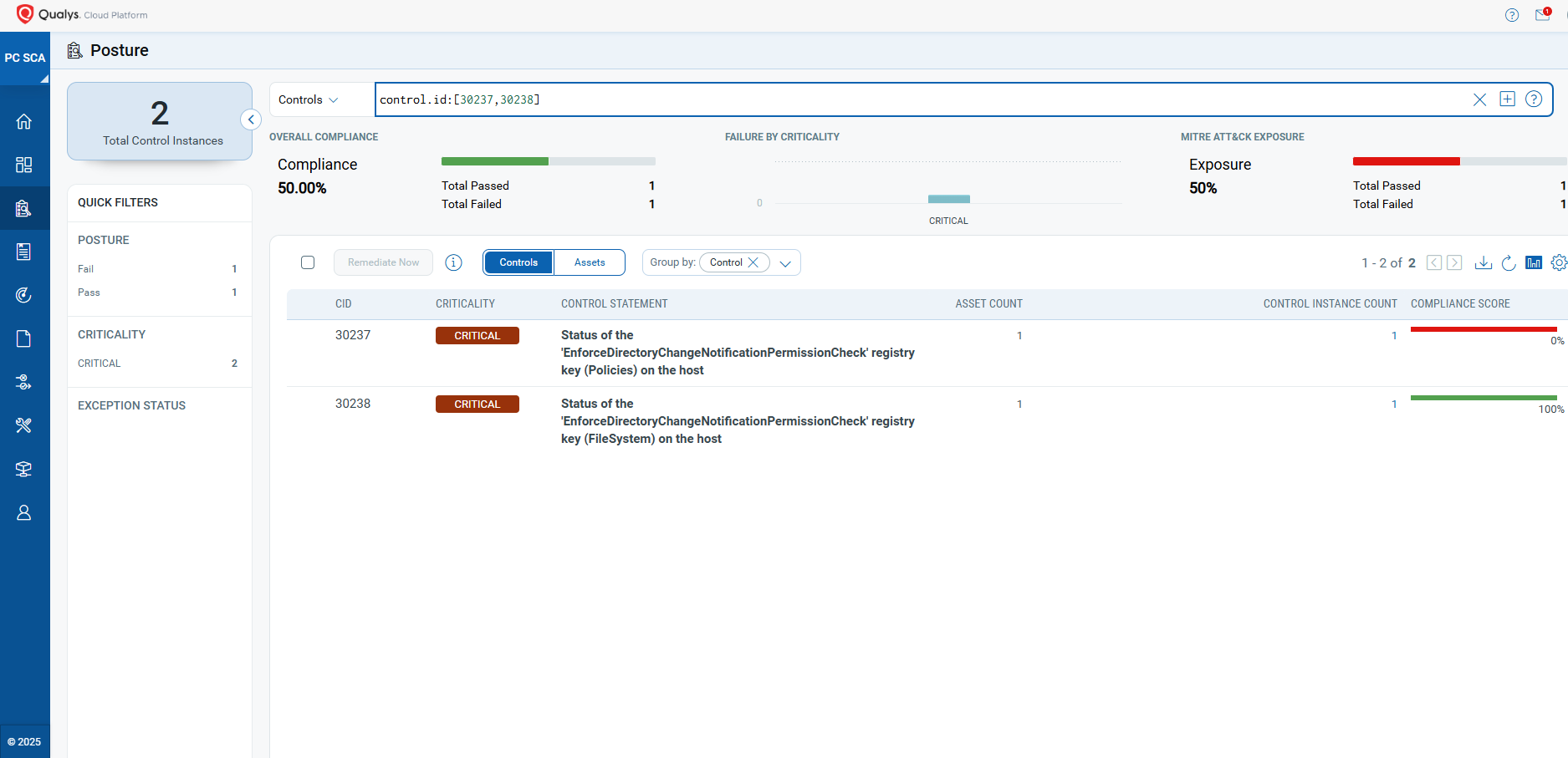
Policy Compliance Control IDs (CIDs):
- 30237 Status of the ‘EnforceDirectoryChangeNotificationPermissionCheck’ registry key (Policies) on the host
- 30238 Status of the ‘EnforceDirectoryChangeNotificationPermissionCheck’ registry key (FileSystem) on the host
The following QQL will return a posture assessment for the CIDs for this Patch Tuesday:
control.id: [30237,30238]
CVE-2025-26647: Windows Kerberos Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
This vulnerability has a CVSS: 3.1 8.1 / 7.1
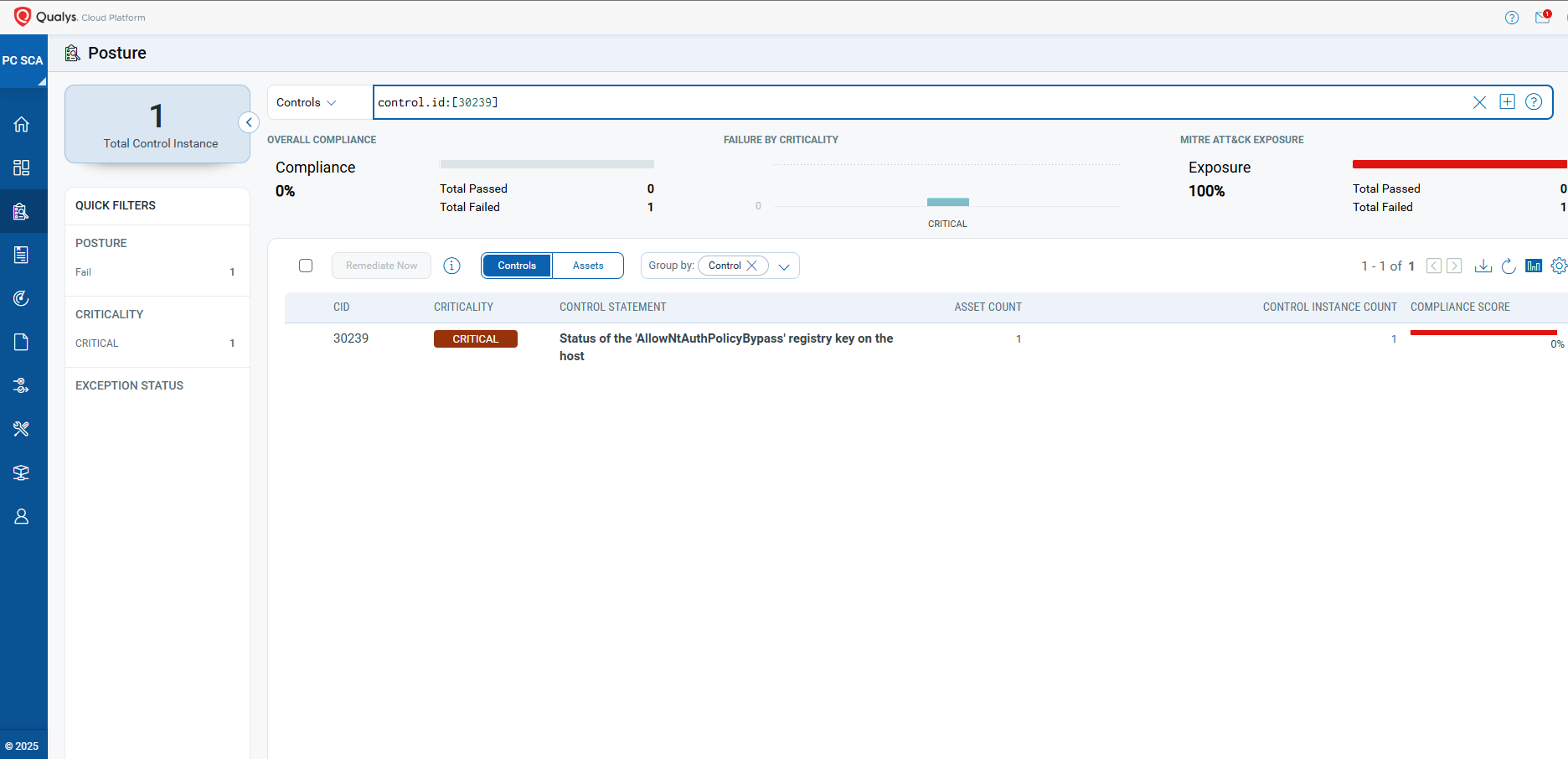
Policy Compliance Control IDs (CIDs):
- 30239 Status of the ‘AllowNtAuthPolicyBypass’ registry key on the host
The following QQL will return a posture assessment for the CIDs for this Patch Tuesday:
control.id: [30239]
CVE-2025-27738: Windows Resilient File System (ReFS) Information Disclosure Vulnerability
This vulnerability has a CVSS: 3.1 6.5 / 5.7
Policy Compliance Control IDs (CIDs):
- 30237 Status of the ‘EnforceDirectoryChangeNotificationPermissionCheck’ registry key (Policies) on the host
- 30238 Status of the ‘EnforceDirectoryChangeNotificationPermissionCheck’ registry key (FileSystem) on the host
The following QQL will return a posture assessment for the CIDs for this Patch Tuesday:
control.id: [30237,30238]

Visit the April 2025 Security Updates page to access the full description of each vulnerability and the systems it affects.
Qualys customers can scan their network with QIDs 100423, 110491, 110492, 383057, 383058, 92234, 92235, 92236, 92237, 92239, 92241, and 92242 to detect vulnerable assets.
Please continue to follow Qualys Threat Protection for more coverage of the latest vulnerabilities.
References:
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/releaseNote/2025-Apr
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-29824
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-26686
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-27752
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-29791
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-27491
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-27745
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-27748
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-27749
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-27480
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-26663
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2025-26670