In February 2020 Patch Tuesday, Microsoft released patches for CVE-2020-0668, an elevation of privilege vulnerability that could allow a local authenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code with elevated permissions.
Description:
It’s an arbitrary file move vulnerability in Service Tracing feature of Windows Operating Systems. This feature provides some basic debug information about running services and modules. This feature can be configured by any local user using “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Tracing” registry.
Using AccessChk from the Windows Sysinternals tools suite, we can check the users Read/Write permissions for the registry key.
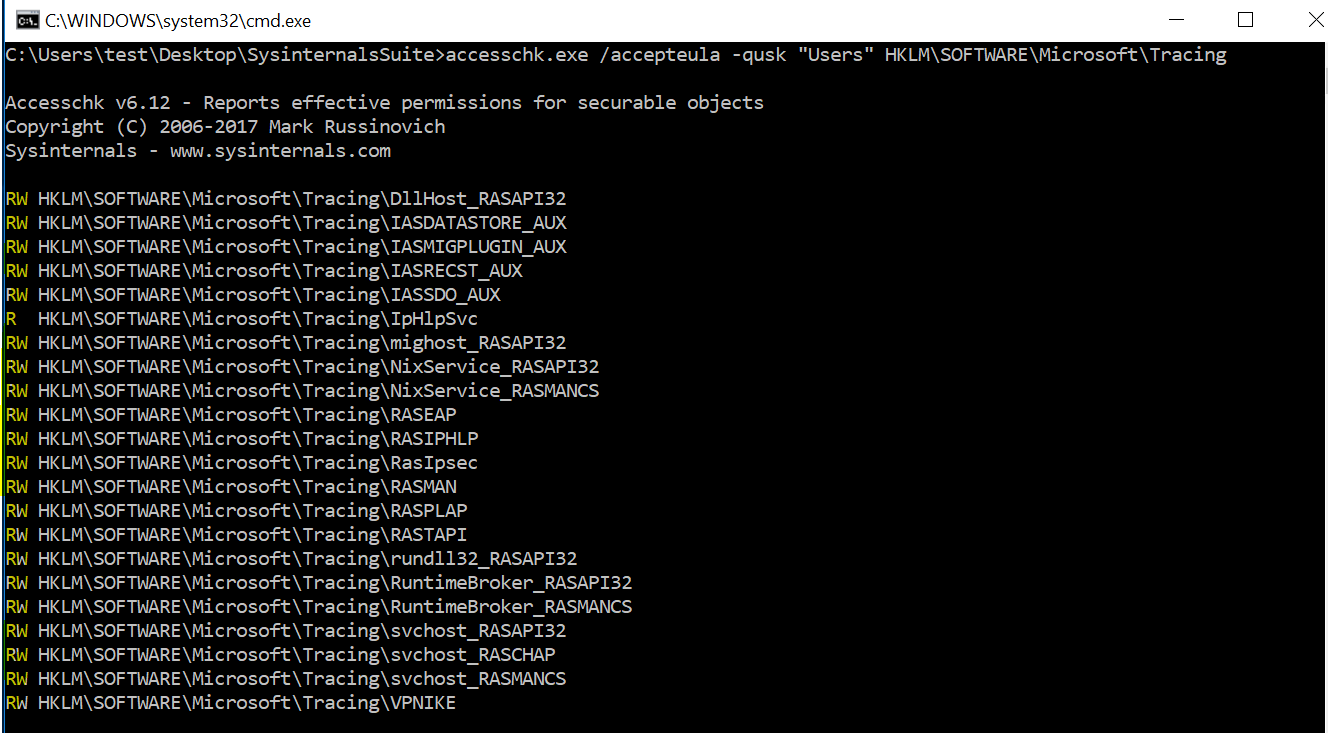
Since all users have access to these registry keys. Here, an attacker can use RASTAPI module’s registry key to exploit the vulnerability.
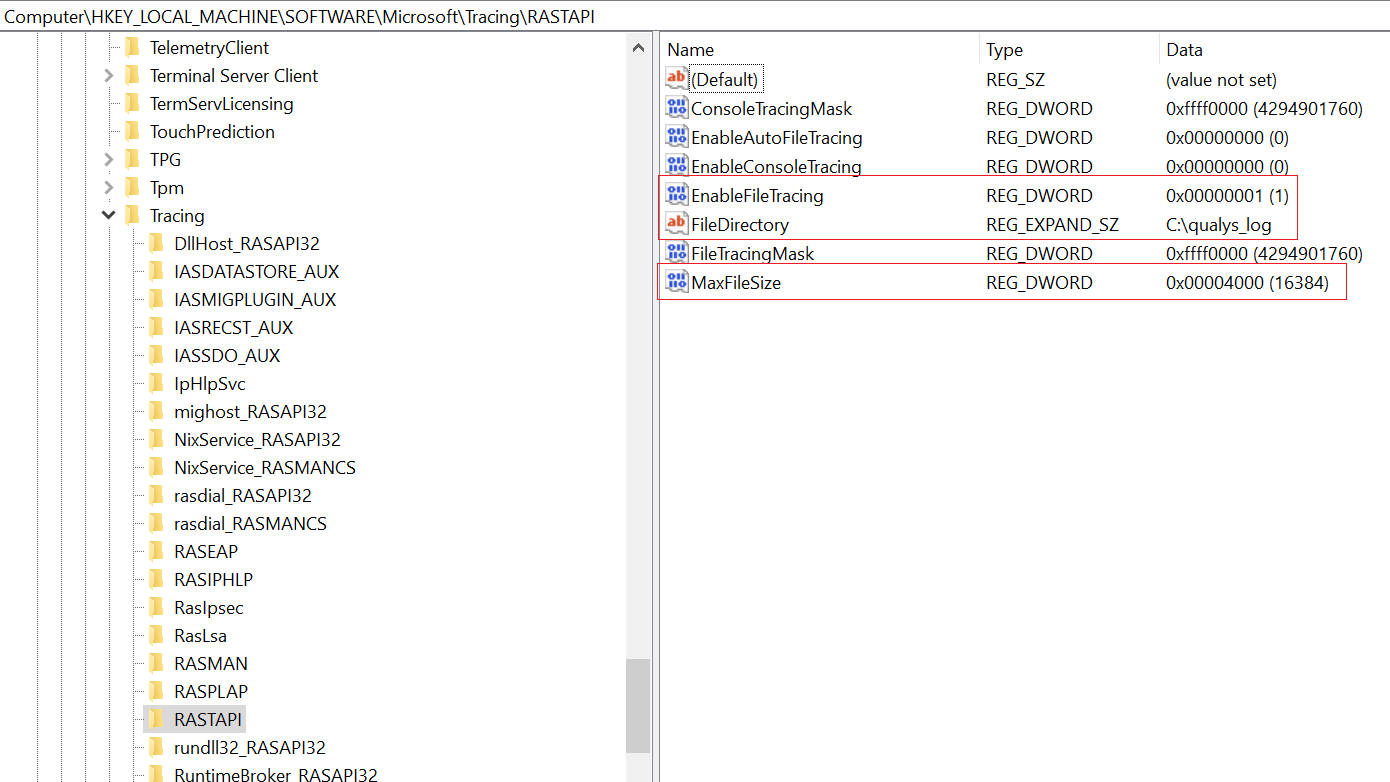
This module is used by the IKEEXT service. One can create log events by initiating dummy VPN connections via rasdial.
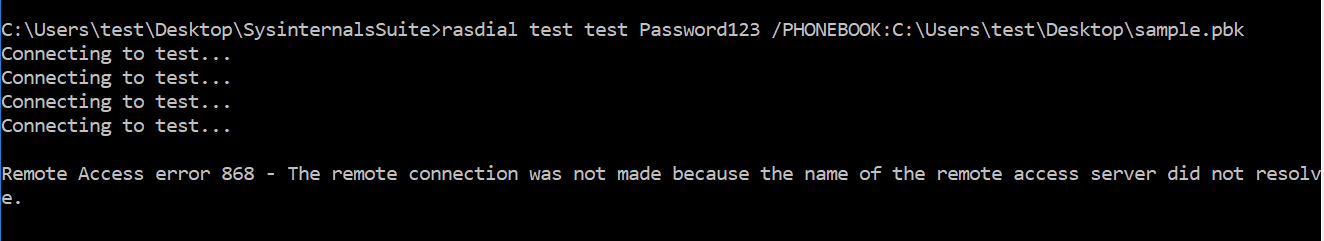
When specified a MaxFileSize of 16,384 bytes, the system will consider the existing log file is full and will move the C:\qualys_log\RASTAPI.LOG to C:\qualys_log\RASTAPI.OLD. The service will also create and write a new C:\qualys_log\RASTAPI.LOG file.
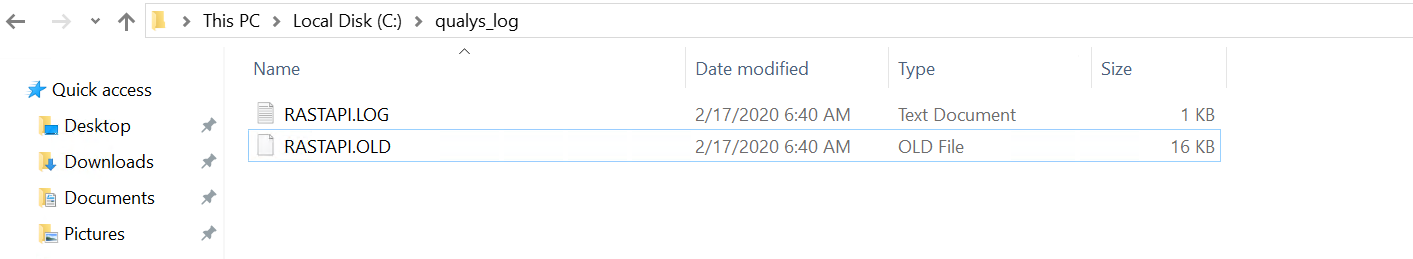
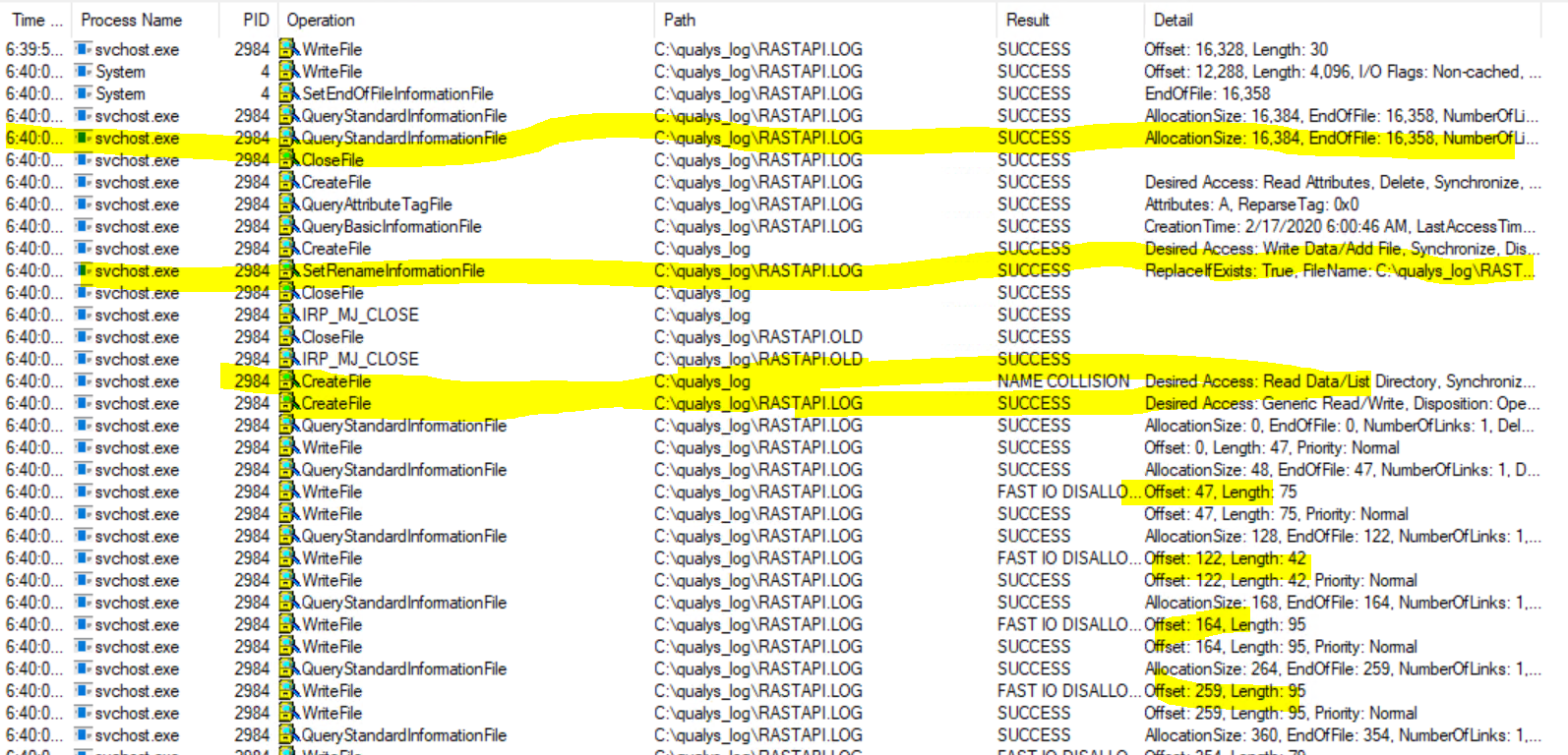
This issue can be leveraged to move a user-owned file to any location on the file system. An attacker can create symbolic links for these log files and may trigger the Update Session Orchestrator service to load the malicious DLL in the context of NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM.
Affected Operating Systems:
Windows 7, Windows 8.1 , Windows RT 8.1, Windows 10 Version (1607,1709,1803,1809,1903,1909), Windows Server 2008 SP2, Windows Server 2008 SP2 (Server Core installation), Windows Server 2008 R2 SP 1, Windows Server 2012. Windows Server 2012 (Server Core installation), Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012 R2 (Server Core installation), Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2016 (Server Core installation), Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2019 (Server Core installation), Windows Server, version (1803,1903,1909) (Server Core Installation)
Mitigation:
Please refer the vendor advisory for more information. Qualys customers can scan their network with QID#91605 to detect vulnerable assets.
Kindly continue to follow on Qualys Threat Protection for more coverage on vulnerabilities.
References & Sources:
https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2020-0668
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-2000-server/cc957864(v=technet.10)?redirectedfrom=MSDN
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-server-2012-r2-and-2012/ff859533(v%3Dws.11)
https://itm4n.github.io/cve-2020-0668-windows-service-tracing-eop/