VMware issued a Security Advisory for Guest-to-Host Escape Vulnerability, VMSA-020-0004.
VMSA-2020-0004 also includes the other two important vulnerabilities in VMware Horizon Client for Windows and VMRC for Windows, (CVE-2019-5543, CVE-2020-3948)
CVE-2020-3947 has assigned to Guest-to Host Escape vulnerability. The vendors labeled it a critical severity bug with a CVSS score of 9.3
What is the Bug?
CVE-2020-3947 is a use-after vulnerability in vmnetdhcp.
vmnetdhcp provides the capability of DHCP communication between the client virtual machine (VM) and the host operating system
Who is responsible?
The vulnerability exists due to a use-after-free error in vmnetdhcp.
As we know Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows us to dynamically assign and manage IP addresses. DHCP process goes through 4 stages while assigning an IP address to the client. These stages are often abbreviated as DORA for Discovery, Offer, Request, and Acknowledgment.
A DHCP client and Server exchange several messages include DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, DHCPRELEASE, and several others.
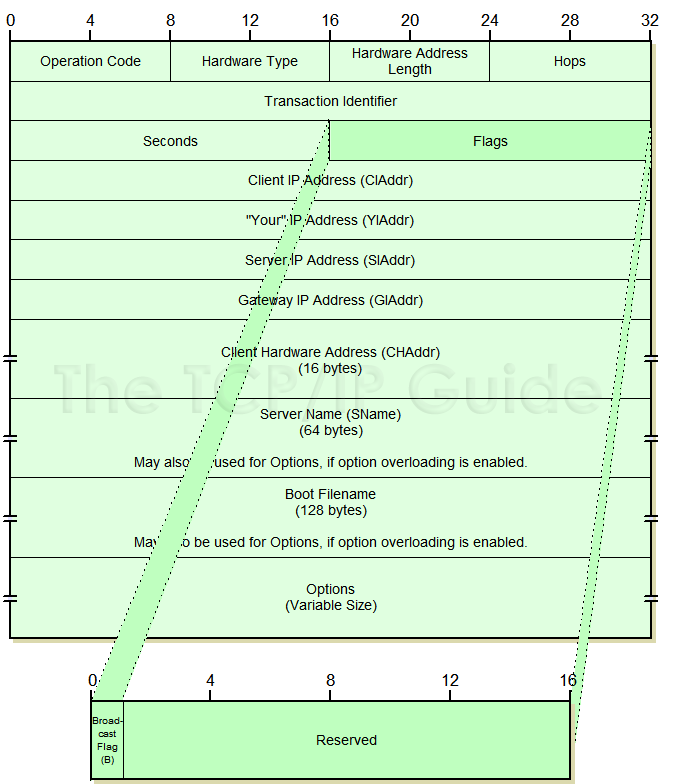
Fig. dhcp_header_structure from www.tcpipguide.com
The Options field begins with the same four-byte “magic cookie” and then contains a number of variable-length option fields. The format of the DHCP Options field is

Fig. dhcp_option_field from www.tcpipguide.com
The DHCP message type option includes the DHCP message type option code (53), the length of the data field (1), and the message type (single byte) can be one of the following values.
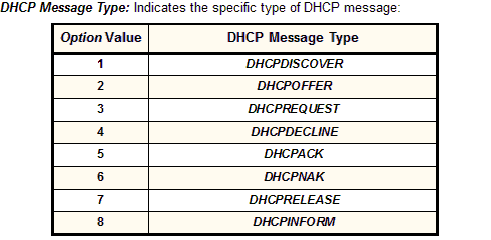
Fig. dhcp_message_type from www.tcpipguide.com
The vulnerable condition occurs when sending a DHCPDISCOVER (Message type 1) message followed by a DHCPRELEASE (Message type 7) message repeatedly to a vulnerable DHCP server.
The vmnetdhcp! supersede_lease (vmnetdhcp+0x3160) function called during the DHCPRELEASE message. A lease structure contains information such as an assigned client IP address, client hardware address, lease duration, lease status, and so on. The supersede_lease function then copies data from one lease structure to another.
The uid field in the lease structure points to a buffer containing the string data from the optionData field of the client identifier option. And the size of this buffer is stored in uid_len field.
The supersede_lease function checks uid fields of the source and destination. It checks whether the string data pointed by the respective lease are equal. If these two strings match, the function frees the buffer pointed to by the uid field of the source lease. To write the lease into an internal table supersede_lease function calls write_lease (vmnetdhcp+016e0).
The lease structure contains a lease duration field. The period of validity of the assignment is called a lease duration and when it expires, the client shall immediately stop using this IP address and stop all communication on the IP network.
The main risk of not complying to this rule is to have more than one device on the network using the same IP address with conflicts on delivering IP frames to the right device (aka duplicate IP address), and in this vulnerability, same condition occurs when DHCPDISCOVER message followed by a DHCPRELEASE message is repeatedly received by the server. Both uid_fields point towards same memory location.
The supersede_lease function does not check for this condition. As a result, when it frees the memory pointed to by the uid field of the source lease, the uid pointer of the destination lease becomes a hanging pointer. Finally, when write_lease accesses the uid field of the destination lease, a use-after-free (UAF) condition occurs (CVE-2020-3947).
Other VMware Vulnerabilities:
Alongside the above, the vendors also fixed two other vulnerabilities in their products.
CVE-2019-5543, CVE-2020-3948 both the vulnerability allows a local user to escalate privileges on the system.
CVE-2020-3948 issue is caused by improper file permissions in Cortado Thinprint, a virtual printing technology.
And for CVE-2019-5543, the folder containing configuration files for the VMware USB arbitration service was discovered writable by all users. As a result, a local user logged into an impacted system could exploit the vulnerability and run commands as any user.
Which products are affected?
For CVE-2020-3947 –
Vmware Workstation and VMware Fusion all versions including 11.5.1
For CVE-2020-3948 –
VMware Workstation and VMware Fusion all versions including 11.5.1
For CVE-2019-5543 –
- VMware Workstation including 11.5.1
- VMware Horizon Client for Windows 5.x and prior to 5.3.0
- VMware Remote Console for Windows 10.x prior to 11.0.0
What can we do?
There is no workaround available for these vulnerabilities. Users must ensure they upgrade to the latest patched versions to stay safe from potential exploitation. Apply the Patch provided by the vendor.
References:
https://www.vmware.com/security/advisories/VMSA-2020-0004.htm
https://www.thezdi.com/blog/2020/4/1/cve-2020-3947-use-after-free-vulnerability-in-the-vmware-workstation-dhcp-component
http://www.tcpipguide.com/free/t_DHCPMessageFormat.htm
https://www.omnisecu.com/tcpip/dhcp-dynamic-host-configuration-protocol-message-options.php
To make your Lockdown days more interesting, Please Continue to Follow Qualys ThreatProtect.
#Stay@Home
#StaySafe