Summary:
In the first week of July,2020, Apache released patches to address two critical vulnerabilities – CVE-2020-9497 and CVE-2020-9498.
Researchers from the Check Point team found these vulnerabilities in FreeRDP and reverse RDP connection of Apache Guacamole.
Description:
According to Apache’s documentation: “guacd is the heart of Guacamole.” Upon startup, guacd listens on TCP port 4822 and waits for incoming instructions from the guacamole-client. At this point it is not mandatory to have authentication, even SSL is not enabled by default. In getting the reverse connection back to Guacamole gateway, “guacd” is the main process that allows attacker to take full control over guacamole server and other interconnected sessions. This has been nicely shown in a short video by the Check Point team. Check Point quotes “Not only that many organizations use this product to connect to their networks, many network accessibility and security products embedded Apache Guacamole inside their own products as well. This list includes: Jumpserver Fortress, Quali, Fortigate, and the list goes on.”
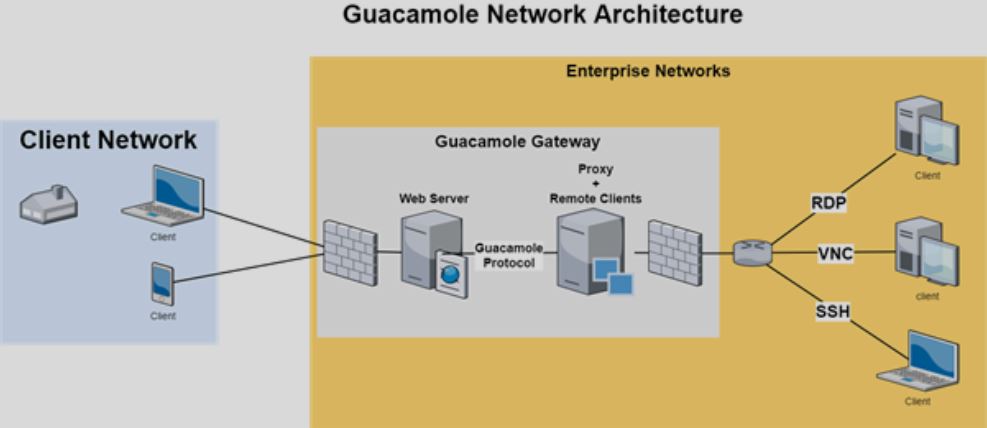
Image Source: Check Point
Guacamole-server can be accessed remotely via protocols such as RDP, VNC, and SSH. The vulnerable components for both the CVEs are notified below.
CVE: CVE-2020-9497
File: protocols\rdp\channels\rdpsnd\rdpsnd-messages.c
Function: guac_rdpsnd_formats_handler()
File: protocols\rdp\channels\rdpsnd\rdpsnd.c
Function: guac_rdpsnd_process_receive()
File: protocols\rdp\plugins\guacai\guacai-messages.c
Function: guac_rdp_ai_read_format()
Above mentioned files and functions are vulnerable components for improper input validation of RDP static virtual channels, which lead to information disclosure events in Apache Guacamole versions earlier than 1.1.0.
CVE: CVE-2020-9498
File: protocols\rdp\plugins\guac-common-svc\guac-common-svc.c
Function: guac_rdp_common_svc_handle_open_event()
CVE-2020-9498 is a memory corruption vulnerability. A nefarious user can exploit this vulnerability to corrupt an RDP server by using dangling pointer in RDP static virtual channel handling, and send out-of-order messages that were by wStream object earlier.
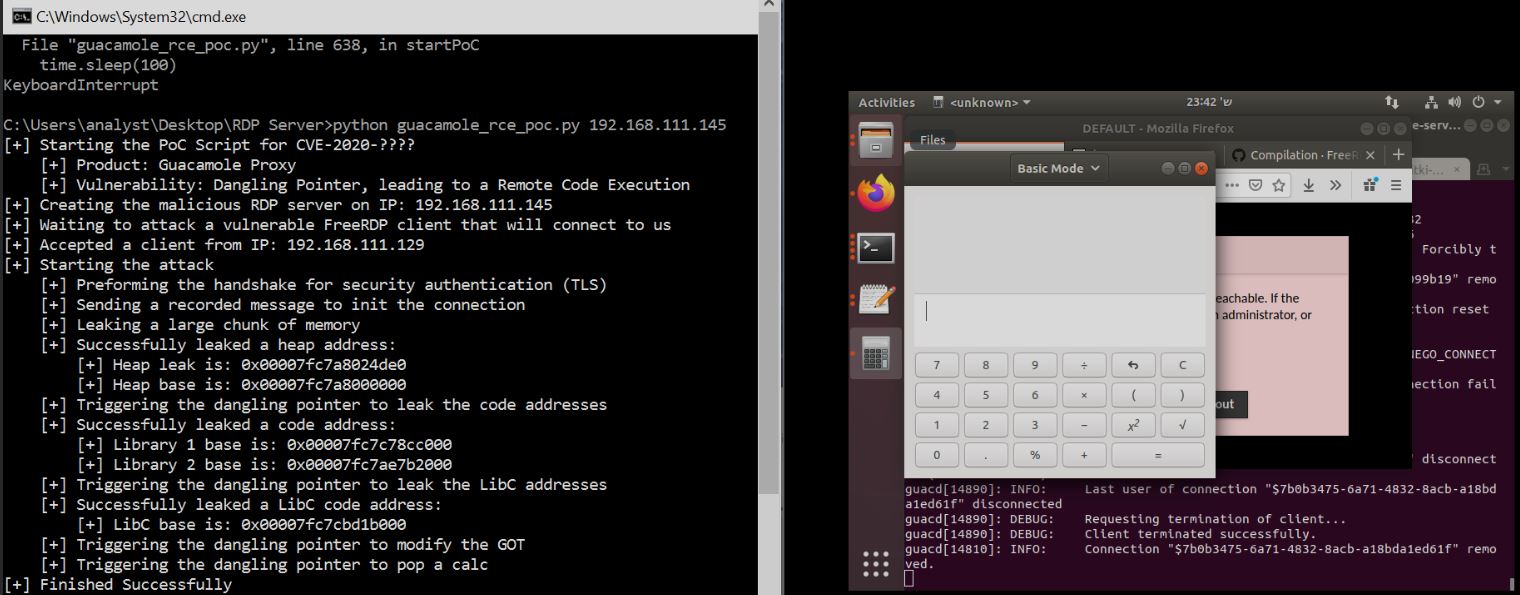
Image Source: Check Point
According to the researchers, “By sending a malicious rdpsnd channel message, a malicious RDP server could cause the client to think that the packet contains a huge number of bytes, which are in fact memory bytes of the client itself. This in turn causes the client to send back a response to the server with these bytes, and grant the RDP server a massive, heartbleed-style, Information Disclosure primitive.”
Affected Products:
Apache Gaucamole v1.1.0 and earlier
Solution:
Apache has released patches to address these issues and has asked customers to update Apache Guacamole to v1.2.0 or later.
Advisory:
Detection:
Qualys customers can scan their network with QID 13828 to detect vulnerable assets. Please continue to follow on Qualys Threat Protection for more coverage on these vulnerabilities.
References & Sources: