A severe bug identified as CVE-2020-1472 with a criticality of 10 is being exploited publicly in the wild. This bug can take over Windows Servers running as Domain Controllers with domain-level privileges from a remote unauthenticated user.
A Dutch team, collectively known as Secura, has published an exploit on Github with a technical writeup. According to this exploit, there are several steps on how an unauthenticated remote user can penetrate Enterprise level Windows Domain Controllers (DC) and leverage admin privileges.
The prime elements of this vulnerability are the weak encryption standards and the authentication process used in the Netlogon protocol. As new Windows Domain Controllers use standard AES-256 as encryption standards, incorrect use of the AES mode results in spoofing the identity of any computer (DC) account and replace it with all zeroes or empty passwords. As the final output replaces all characters of the password with zeroes, this bug is also well-known as “zerologon”.
Series of steps of exploiting Microsoft Netlogon Service goes like this:
- Firstly, almost 256 or more brute force attempts are carried out to connect to the DC’s Netlogon service
- Once successful, the client and the server exchange random 8-byte nonces (challenges) in encrypted form.
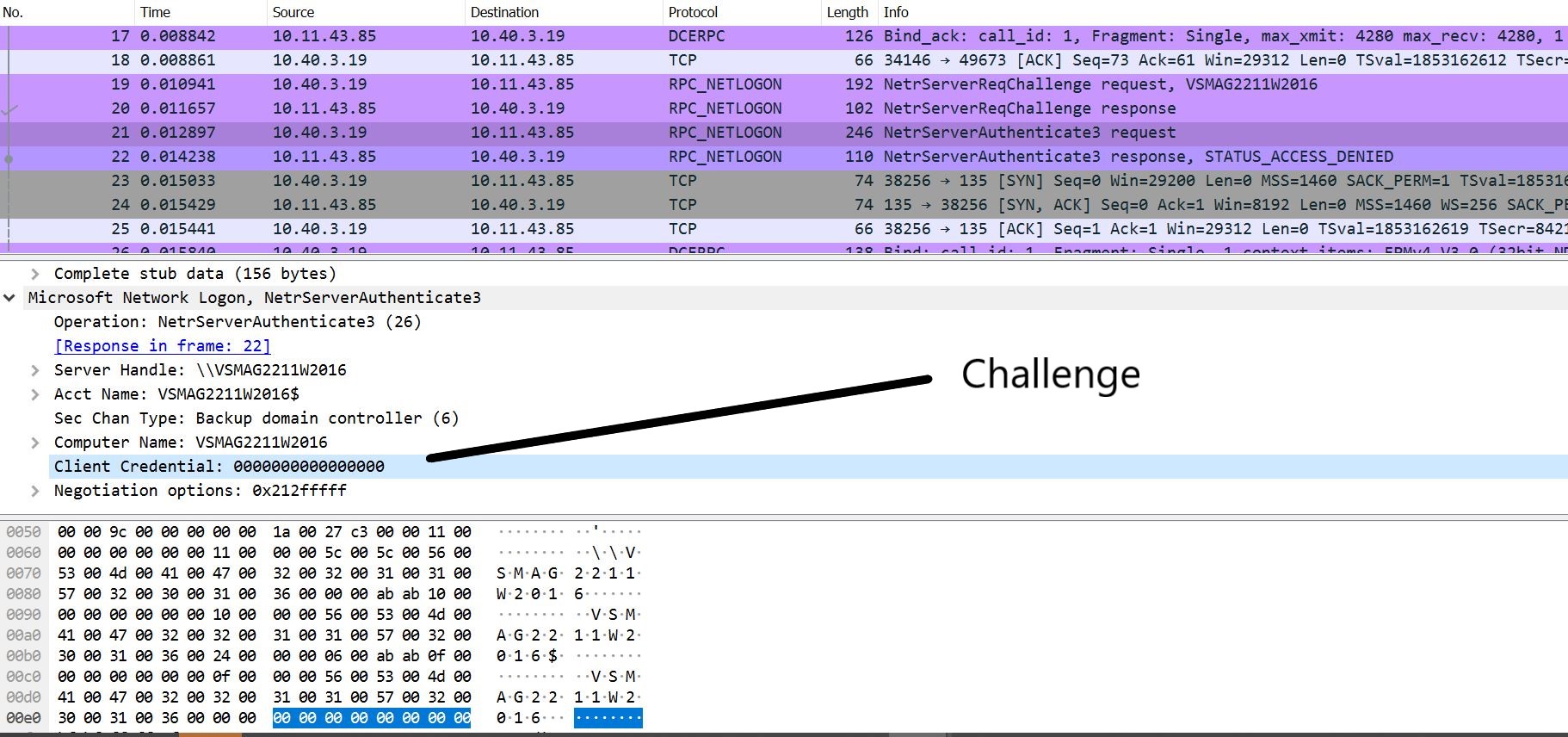
Image Source: Qualys Labs
- STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED error is observed if the authentication request fails while sending the challenge, which is displayed as This error can appear multiple times until the authentication is successful.
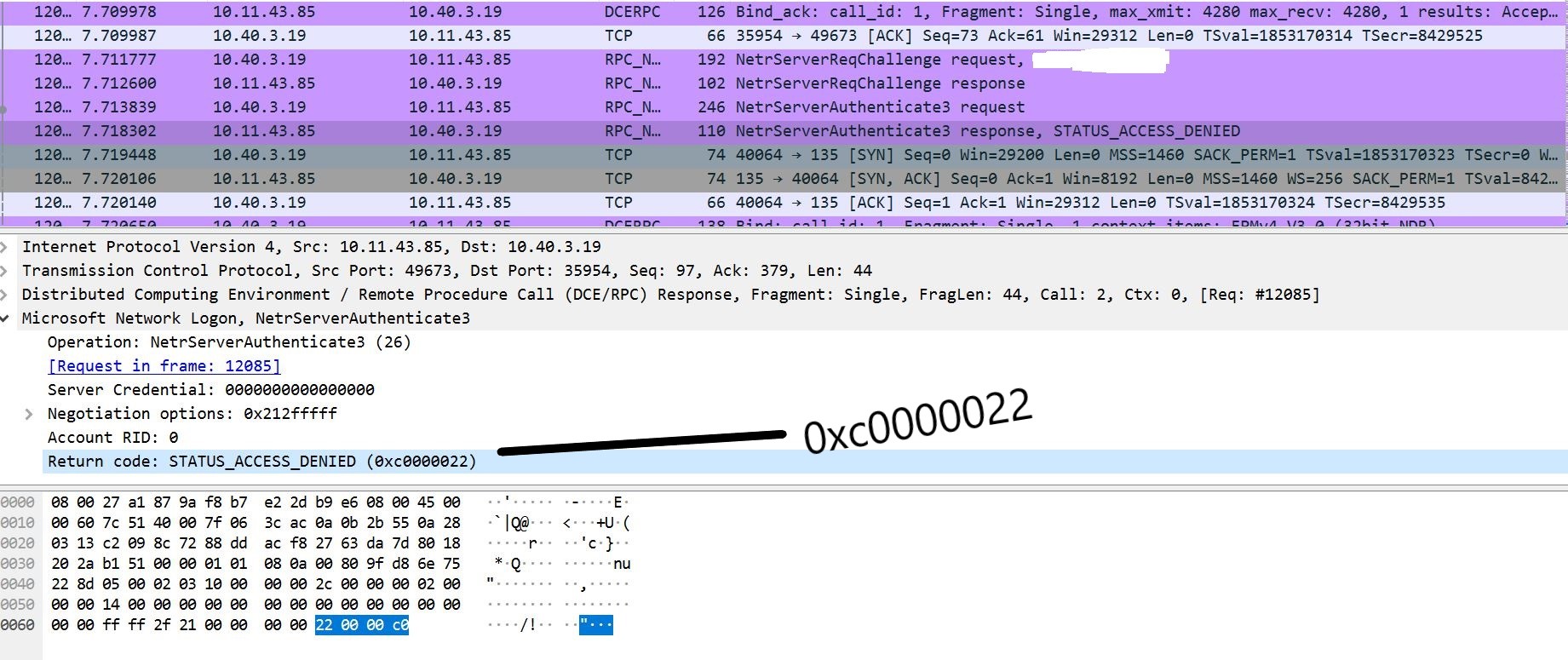
Image Source: Qualys Labs
- The brute force technique keep authenticating until successful. Expected average number of attempts needed is 256. Microsoft network Logon NetrServerAuthenticate3 returns STATUS_SUCCESS with all zeroes indicating “Zerologon” has been successful.
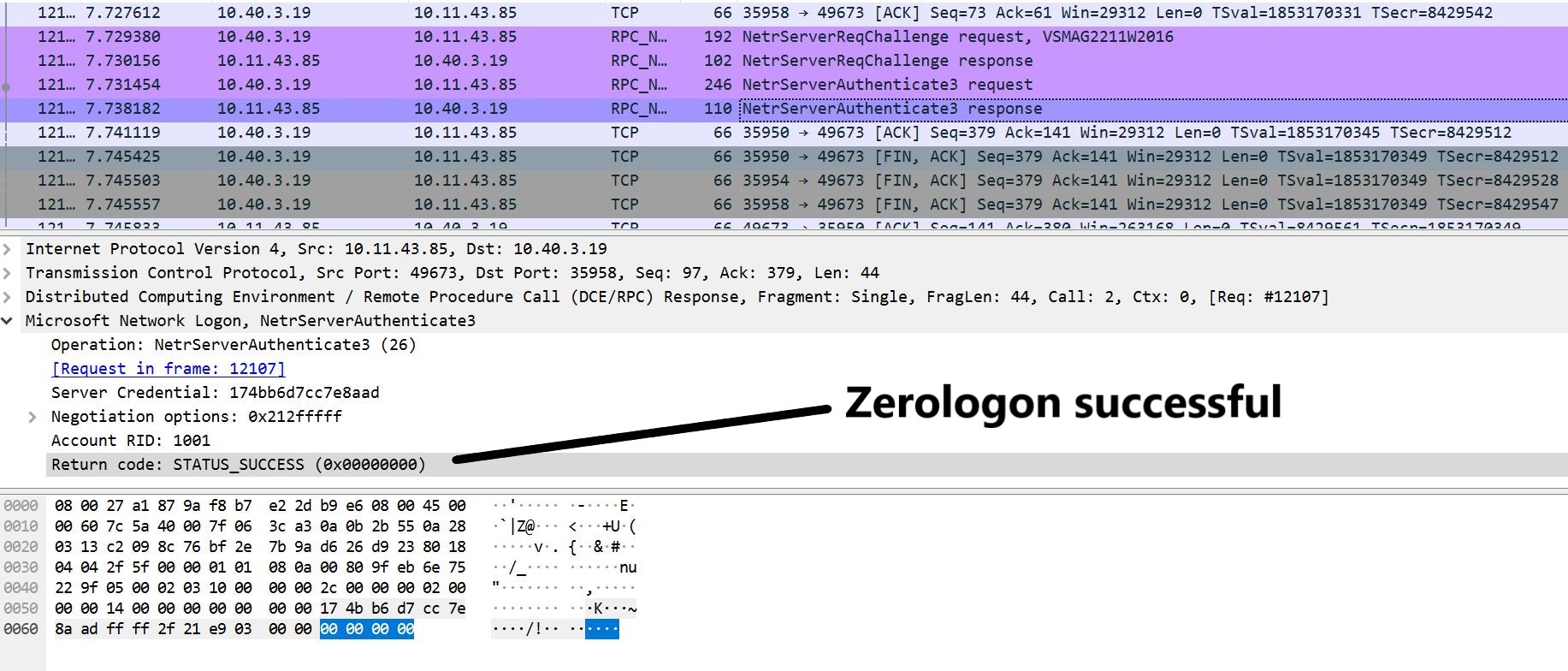
Image Source: Qualys Labs
Once the exploit is successfully executed, an unauthenticated user can gain Domain Admin privileges on the vulnerable DCs.
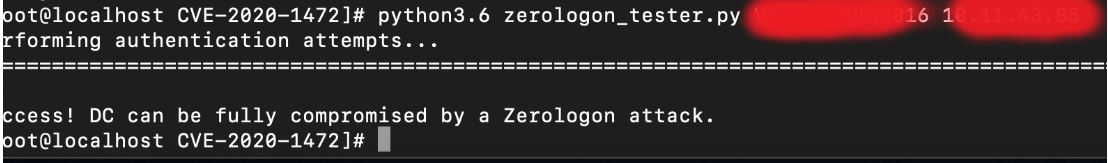
Image Source: Qualys Labs
Affected Products
- Windows Servers 2008
- Windows Servers 2012 R2
- Windows Servers 2016
- Windows Servers 2019
A complete list of affected devices is available on Microsoft’s August 2020 security advisory.
Solution
Users are advised to review their Microsoft Windows installations with Microsoft’s August 2020 security advisory mentioned above. For Windows devices, a patch to be published in Feb 2021 would disable the “enforcement mode” by default.
Detection
Qualys customers can scan their network with QID 91668 to detect vulnerable assets.
Please continue to follow Qualys Threat Protection for more coverage on latest vulnerabilities.
References
https://www.secura.com/pathtoimg.php?id=2055
https://github.com/SecuraBV/CVE-2020-1472
https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2020-1472