In the first week of August, Pulse Secure published an advisory and patches for vulnerability, CVE-2021-22937. This is a post-authentication, distant codification execution (i.e.,Remote Code Execution) vulnerability that exists on Pulse Connect Secure virtual backstage web (i.e.,VPN) appliances.
This vulnerability, classified as CWE-434 and a CVSSv3 of 9.1, is an uncontrolled archive extraction vulnerability that exists on the Pulse Connect Secure appliance. The vulnerability allows an authenticated head to constitute arbitrary executable files to the “/home/runtime/tmp/tt/” directory. This unrestricted file upload vulnerability is due to a flaw in the way that archive files are extracted in the administrator web interface.
While there is no direct PoC for CVE-2021-22937, Warren, a security researcher from nccgroup included a screenshot of the changes he made to his PoC for CVE-2020-8260 in his technical advisory for CVE-2021-22937, so we expect to see modified exploit scripts soon.
A Proof of Concept was developed to achieve remote code execution as the root user, simply by changing a single POST parameter variable in the original CVE-2020-8260 exploit.
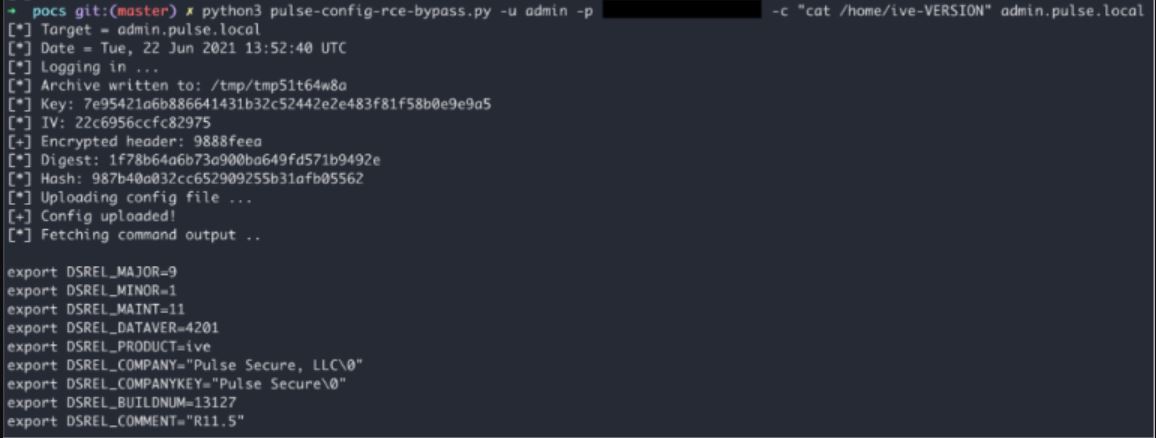
Image Source: nccgroup
Pulse Secure added validation to guarantee archives lone incorporate “expected files” to code CVE-2020-8260, but this validation is not used to each of the archives, leaving an opening for attackers. At the time of publishing this blog, active attacks were observed in the wild as per Pulse Connect Secure.
Affected products
Pulse Connect Secure before 9.1R12
Mitigation
The vendor, Pulse Connect Secure, has published an advisory to address this severe issue. More information on version 9.1R12 can be found in the Product Release Notes and Technical Support Bulletin TSB44856.
Qualys Detection
Qualys customers can scan their network with QID 38847 to detect vulnerable assets.
Please continue to follow Qualys Threat Protection for more coverage on the latest vulnerabilities.
References and Sources
- https://kb.pulsesecure.net/articles/Pulse_Security_Advisories/SA44858
- https://research.nccgroup.com/2021/08/05/technical-advisory-pulse-connect-secure-rce-via-uncontrolled-archive-extraction-cve-2021-22937-patch-bypass/
- https://cyberfishnews.com/cve-2021-22937-remote-code-execution-patch-bypass-in-pulse-connect-secure-47735.html?__cf_chl_jschl_tk__=pmd_806e3c692b27f63f89cbea33be087bd89e6c4595-1628237427-0-gqNtZGzNAjijcnBszQa6